Agentic AI changes work by planning, calling tools, and acting for people. Teams already test agentic AI in browsers and backend systems. You will see more pilots this year, and with pilots comes real risk. autonomous AI systems need rules and clear accountability.
Here is the thing, this guide maps what agentic agents do, where they appear, the new threats they bring, and concrete guardrails teams can deploy today. Expect plain language, a vendor snapshot table, a risk matrix, and checklist templates you can copy. Read this to get your teams aligned.
1. What agentic AI actually is, and why it matters
Agentic AI describes systems that break tasks into steps, plan, and call tools to finish work. Unlike chatbots that only respond, agentic AI performs actions across systems. This matters because autonomy changes who touches data, who signs contracts, and who is liable for mistakes.
What this means is your product can scale work and also scale failure. autonomous AI systems can speed testing, ticket handling, research or internal workflows, yet they can also act without human pause. Treat autonomy as a capability, not a magic button.
what is agentic AI and how does it differ from chatbots
Agentic models orchestrate subtasks, maintain memory, and call APIs or browser commands. Chatbots reply in text, but AI agents in production take action. That core difference shifts engineering, security, and compliance work.
2. Quick snapshot: real world pilots and production examples
Google and others have pushed agentic features into browser demos that actually move through pages to complete tasks. These demos show agents can fill forms, test UI, and perform chained actions. The Verge and Google coverage documented browser agents and demos.
Startups like Adept, and a wave of enterprise pilots, show real workflows where agents open apps, gather data, and push changes. These pilots prove value and prove risk too. Expect more pilots in healthcare, finance and internal ops this year.
examples of agentic AI pilots in enterprise 2025
Enterprises test agents for research automation, help desk resolution, compliance checks, and internal ops. Early pilots showed time saved and surprising edge cases where agents abused connectors. That tension defines the current real-world path.
3. How agentic systems are architected
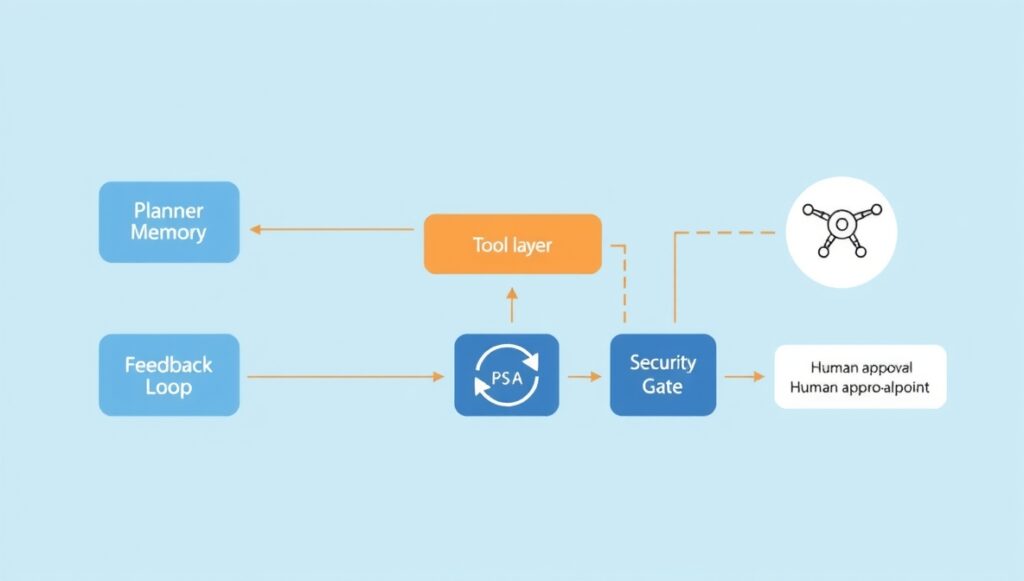
Agentic systems combine a planner, memory, and tool layer. The planner decides steps, memory stores state across tasks, and tools let agents act in apps and APIs. Engineers must design each layer with constraints, safeguards, and audits in mind.
What this really means is you need a modular design with clear interfaces between planner, memory, and tools. Treat each module as a security boundary and add provable checks before any action reaches production.
building test harnesses for emergent behavior in agentic AI
A test harness simulates chains of actions, adversarial prompts, and memory poisoning attempts. Automated scenarios validate expected outcomes across state changes. Good testing finds emergent errors early before they reach users.
4. The immediate operational risks to map

Agentic deployments amplify cascading hallucinations, unauthorized actions, and stealthy data exfiltration risk. A hallucination that issues a wrong command may cascade through systems, creating multi-step failures that are hard to unwind.
Operator safety is often overlooked while agent hijacking remains a realistic threat. When an agent calls external tools, it may touch secrets or move data. Map these risks, and treat state and connectors as prime attack surfaces.
how to prevent AI agents from exfiltrating data
Prevent exfiltration by limiting connectors, scanning outputs for secrets, and setting token scopes tightly. intent auditing helps detect suspicious action sequences before data leaves your secure environment.
5. Security failure modes that are new or amplified
Agentic systems introduce memory poisoning, tool misuse, and unexpected lateral movement on top of classical threats. Memory poisoning corrupts context gradually, leading to stealth drift that typical prompt checks may miss.
Tool misuse turns helpful connectors into attack vectors, and resource exhaustion attacks can force unintended behaviors. You must secure the tool layer, enforce quotas, whitelists, and signed calls for every external operation.
identity and agent hijacking scenarios
Agent identity vulnerabilities may allow merged operational identities across systems. If an attacker abuses that, they can perform lateral moves. agent observability must record identity provenance.
6. Governance, accountability, and legal angles
Accountability splits across vendor, integrator, and operator, and regulation is catching up unevenly. The IAPP highlights professionalizing AI governance 2025, and firms must document decisions, audits, and sign-offs before deployment.
Contracts should define autonomous actions, damage caps, and audit access. Insurance may cover system failures, but not governance breakdowns. Build a ledger of intent and approval for every agent capable of action. AI safety for enterprises starts in legal and procedural work.
legal liability for autonomous AI actions, who is accountable
Liability often rests with the deployer when agents act on behalf of a business. Vendors must offer traceability, and legal teams should define acceptable automation scopes before rollout.
7. Practical guardrails product teams can implement today

Use human in the loop gates for any action that affects data, permissions, or transactions. Gate each critical action step with human approval. intent auditing captures decision rationale and makes post-mortem review possible.
Also enforce capability limits, tool whitelists, and per-task allowed operations. Keep agent goals narrow, require signed outputs for calls, and log input and output with full context. These rules reduce surprises and help with accountability.
human in the loop best practices for autonomous AI systems
Provide fast review UIs, timebox human checks, and require signoff only on actions above risk thresholds. Rotate reviewers and audit logs after human overrides to prevent complacency.
8. Testing strategies and test harnesses for emergent behavior
Your test harness must include scenario catalogs, adversarial prompts, and regression checks for emergent agent behavior. Simulate long-running tasks, memory corruption, and tool errors to find weak points before production.
Fuzz connectors, run canary deployments, and measure failure cascades across modules. A continuous testing pipeline should run before every update, catching surprises before release.
building test harnesses for emergent behavior in agentic AI
Design evaluations that replay realistic sessions, inject edge inputs, and verify that intent auditing flags anomalies. Track metrics like false action rate and time to human override.
9. Observability, logging, and forensic readiness
Agent observability must capture planner decisions, memory snapshots, tool calls, user approvals, and errors. Immutable logs and signed prompts give you a chain of evidence. agent observability is nonnegotiable for production systems.
Store logs in write-once media, include provenance metadata, and ensure forensic playbooks can reconstruct states and replay actions. That way audits or legal asks can be answered with clarity.
observability and forensic logging for AI agents
Log planner inputs, chain reasoning steps, and tool responses. Use cryptographic signing to prevent tampering and tie evidence back to an accountable identity.
10. Data governance and access controls

Enforce least privilege for connectors, token scopes, and APIs. Use data minimization to reduce attack surface. Policies on retention and memory scope help mitigate data exfiltration risk.
Do not allow secrets or sensitive data to flow through agent memory. Use ephemeral tokens for safe actions and require approval for accessing persistent data. Treat memory fields with access control lists and rollback snapshots.
securing tool integrations used by agentic systems
Require tool whitelisting for agents, quotas, and output validation. Only allow signed, auditable interactions with third-party APIs or services.
11. Runbooks, incident response, and kill switches
Create incident classification schemes including hallucination-driven actions and tool misuse. A kill switch must immediately revoke agent write privileges. Runbooks should define roles, escalation paths, and recovery steps.
Post incident audits must record timeline, root cause, and remediations. Train your teams through regular drills to shut down agents and preserve logs for further analysis or legal review.
incident response for autonomous systems that take actions
Classify incident severity by business impact. Empower one role to suspend agent actions immediately. Document every decision for follow up.
12. Vendor evaluation checklist for agentic features
In vendor evaluations ask for audit trail support, memory control, signing of outputs, and ability to revoke actions. Confirm they support tool whitelisting for agents, rate limits, and fine-grained RBAC for connectors.
Insist on a demo replicating attack scenarios. Score vendors on transparency, observability, contractual liability, and rollback ability. Choose ones that log decisions clearly and support safe resets.
vendor questions for evaluating agentic AI platforms
Require proof of signed outputs, memory isolation, and forensic support. Hold vendors to SLA uptime and clear remediation timelines when things go wrong.
13. Business case and measurable KPIs
You want metrics like tasks automated per day, error rate, override time, and cost of human review. Also build scenarios for failure cost—such as what happens if a cascading hallucination triggers payments.
Track pilot KPIs such as automation rate, false action rate, and mean time to override. Use those data points to judge whether scaling AI agents in production makes sense or introduces excessive risk.
ROI and cost tradeoffs for deploying agentic AI in production
Weigh productivity gains against oversight and incident remediation costs. Even strong wins can be erased by unexpected failures if guardrails are weak.
14. Regulatory and policy watchlist
Legislation is catching up in 2025. Many states are proposing AI usage rules, disclosure obligations, and oversight requirements. Keep a policy map, and include state and national trackers like NCSL.
International and sector laws lag or vary. Health and finance already have tighter rules. Cross-border rules complicate agentic workflows passing data between regions. Build compliance into your agents from day one.
AI governance checklist for product and security teams 2025
Create a living regulatory map. Maintain an audit ledger. Mandate local legal review when agents perform high risk actions. Refresh the map quarterly to catch new laws.
15. TLDR checklist and templates
Every pilot must start small, scope tightly, and demand signed, auditable actions. Use human in the loop gates for critical actions, build test harnesses that simulate memory or tool attacks, and embed a kill switch in every deployment.
Here is a vendor snapshot and risk table for your internal docs:
| Vendor or Topic | What they show or offer | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|
| Google Gemini browser agents | Browser driven actions in demo | Shows real agentic browser capability for UI tasks. |
| Adept | Workflow automation with web understanding | Demonstrates planning, memory, tool orchestration. |
| Security research | Lasso reports on agentic threats | Highlights new threat models you must defend. (lasso.security) |
| Key Risk | Immediate mitigations |
|---|---|
| cascading hallucinations | Gate changes, rollback points, intent logs |
| agent hijacking | Identity provenance, signing, RBAC |
| data exfiltration risk | Connector limits, token scopes, scanning |
“Treat agentic deployments like launching a small satellite. The tech is powerful, the recovery is hard, and every parameter matters.”
That phrase captures why planning, testing, and logs are essential.
16. How to Use AEO strategies (Snippets, Voice, ChatGPT, SGA)
Here’s the thing: your content should work for Google Snippets, voice queries, ChatGPT style answers, and SGA (Search Generative AI). Use short, clear Q&A designed for featured snippets and voice surfaces. Then embed them in your SEO structure and internal linking. Also optimize for GMB local if relevant. Don’t just write long prose; answer questions directly and concisely.
5 Q&A for voice search, snippet ranking, and ChatGPT style
Q1: What is agentic AI?
Agentic AI is a system that takes multi-step actions, calls tools, and executes tasks automatically rather than only replying with text.
Q2: What are major agentic AI risks?
Risks include cascading hallucinations, data exfiltration risk, and agent hijacking when agents misuse connectors or get compromised.
Q3: How to audit actions taken by AI agents?
You use intent auditing, record rationale, sign output, and keep logs that tie actions to accountable identities (human or system).
Q4: What guardrails should product teams use with agentic AI?
Enforce human in the loop gates, restrict tools via tool whitelisting for agents, use runtime policy enforcement, and test emergent behavior before rollout.
Q5: Who is legally accountable when autonomous AI systems act?
Liability generally lies with deployers. Vendors must support observability, traceability, and contractual frameworks defining limits and responsibilities.













Leave a Reply